GPT (GUID Partition Table)

GPT (GUID Partition Table) is a modern disk partitioning standard that replaces the legacy MBR (Master Boot Record) system. It defines how partitions and data are structured on a storage device—such as SSDs or HDDs—providing greater reliability and flexibility for today’s operating systems.
Unlike MBR, which typically supports disks up to about 2TB when using traditional 512-byte sectors, GPT supports larger disks and allows nearly unlimited partitions, making it the preferred option for high-capacity drives.
Table of Contents
How GPT Works
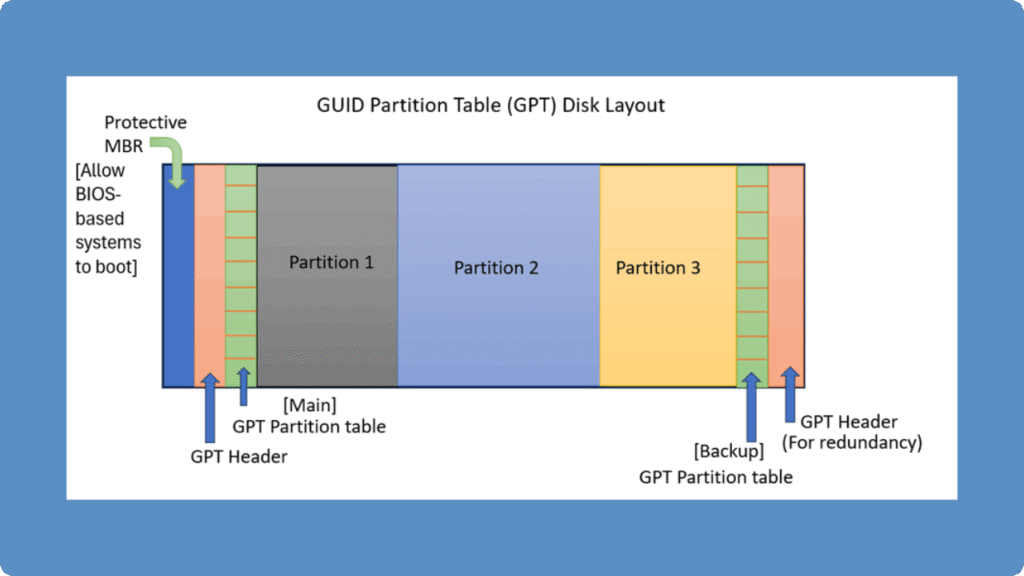
A GUID Partition Table-formatted drive contains four key structures:
1. Protective MBR – Prevents older tools from misidentifying the disk.
2. Primary GPT Header – Stores layout data and partition entries.
3. Partition Entries – Define each partition’s type, size, and ID.
4. Backup GPT Header – Located at the end of the disk to ensure redundancy.
Because this partition table keeps duplicate metadata, even if the primary header is damaged, the system can usually restore the disk layout from the backup header—a key improvement over MBR.
Benefits of the Partitioning Standard
The GUID Partition Table provides several advantages over MBR for both IT professionals and everyday users:
Larger Disk Support: Handles disks exceeding 2TB without issue.
More Partitions: Supports up to 128 primary partitions on Windows.
Redundancy and Integrity: Backup partition tables improve recovery chances.
CRC Protection: Uses Cyclic Redundancy Check to verify data integrity.
Wide Compatibility: Fully supported by Windows 10/11, macOS, and Linux (UEFI-based).
These benefits make this format ideal for enterprise storage, modern SSDs, and large-capacity drives.
Limitations of the Format
Despite its advantages, the GUID Partition Table has a few practical limitations:
Legacy System Incompatibility: Older BIOS systems cannot boot from GPT disks.
Recovery Complexity: If both primary and backup headers are damaged, manual recovery is required.
Conversion Risk: Changing MBR to GPT without a backup may cause data loss.
Always back up important files before repartitioning or converting your disk.
GPT vs. MBR: Key Differences
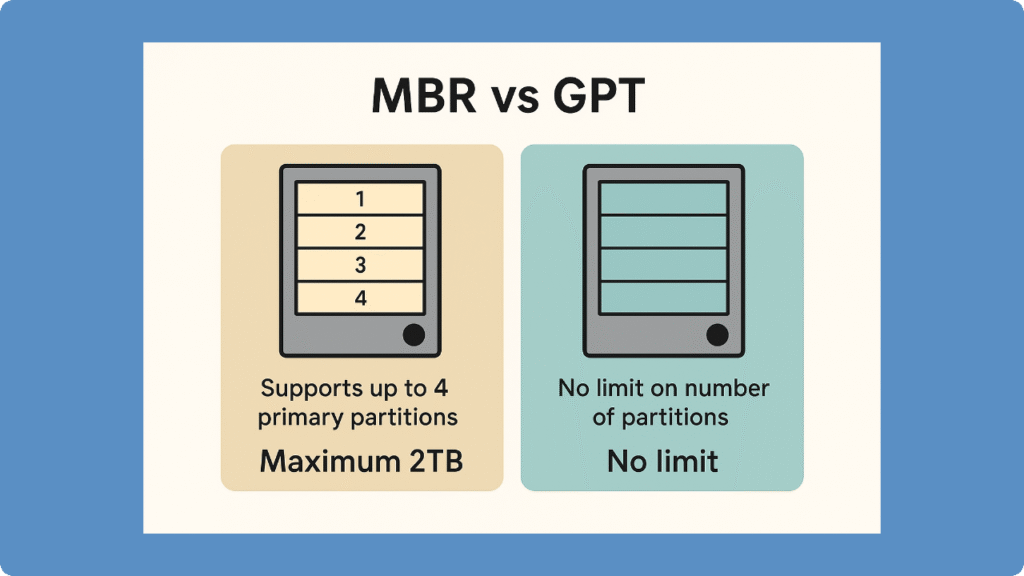
Feature | GUID Partition Table | Master Boot Record |
Max Disk Size | Over 2 TB (no sector limitation) | About 2 TB with 512-byte sectors |
Partition Limit | Up to 128 | 4 Primary |
Redundancy | Yes (Backup Header) | No |
Integrity Check | CRC Protection | None |
Boot Compatibility | UEFI | Legacy BIOS |
How to Initialize a Disk to GPT Format
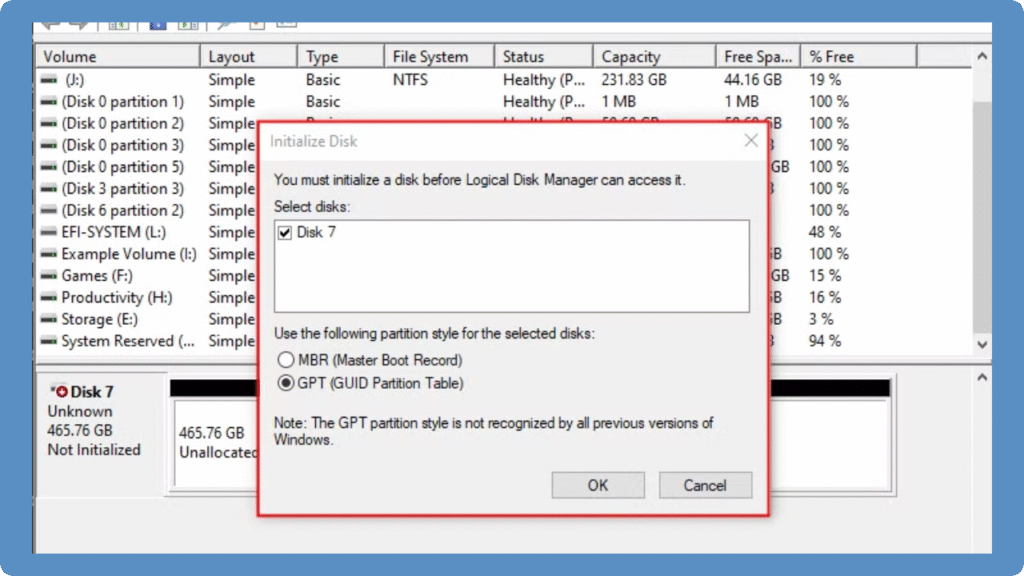
If your new drive is not recognized or shows as “unallocated,” it may need to be initialized as a GUID Partition Table disk. Converting or initializing a disk to GUID Partition Table allows modern systems with UEFI firmware to access its full capacity and create more than four partitions. Follow these steps to safely initialize a disk to the GUID Partition Table format:
1. Open Disk Management
Right-click This PC or My Computer, select Manage, then open Disk Management under Storage.
2. Locate the Uninitialized Drive
Find the drive marked as “Unknown” or “Not Initialized” at the bottom panel.
3. Initialize the Disk
Right-click the disk label (e.g., Disk 1) and select Initialize Disk.
In the dialog box, choose GPT as the partition style.
4. Create New Volumes
After initialization, right-click the unallocated space, choose New Simple Volume, and follow the setup wizard.
5. Format and Assign a Drive Letter
Select the desired file system (NTFS or exFAT), assign a drive letter, and complete the process.
Once completed, the drive will be fully accessible as a GUID Partition Table disk, supporting larger capacities and improved reliability compared to MBR.
Recover Your Drive Safely
If your GUID Table partition is lost or unreadable, don’t worry—you can still recover your data securely.
👉 Download Magic Data Recovery to restore GPT partitions safely with read-only scanning and high success rates.
Supports Windows 7/8/10/11 and Windows Server
Conclusion
The GPT has become the modern standard for managing disks in both consumer and enterprise environments. Compared with MBR, GPT offers greater capacity, enhanced redundancy, and better compatibility with UEFI-based systems. If your new drive isn’t recognized or appears unallocated, initializing it as a GUID Partition Table disk ensures optimal performance and full storage utilization.
For those handling important data or transitioning from older drives, always use trusted software to manage partitions safely. Tools like Magic Data Recovery provide a reliable way to recover data from GUID Partition Table drives if issues ever occur.
Take control of your storage — initialize your disks with GPT and keep your data secure with Amagicsoft.
FAQ About GPT
1. What is GUID Partition Table?
2. What is the difference between GPT and MBR?
3. Can I use GUID Partition Table Disk on Windows or macOS?
4. Can I convert MBR to GPT without losing data?
5. Why does my disk show as “unallocated”?
6. Which disk type is better for SSDs or HDDs?
7. What happens if the GPT header is corrupted?
8. How can I check if my disk uses MBR?
9. Can GUID disks be used for data recovery?
10. Is GUID Partition Table suitable for external or USB drives?
Erin Smith is recognized as one of the most professional writers at Amagicsoft. She has continually honed her writing skills over the past 10 years and helped millions of readers solve their tech problems.



